CompletableFuture 详解
了解 Future的同事,都清楚Future没法直接对多个任务进行链式、组合等处理,需要借助并发工具类才能完成,实现逻辑比较复杂。同时,获取结果的get()方法也会阻塞当前线程。
CompletableFuture常用方法归类:
| 分类 | 方法 | 说明 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 异步执行一个线程 | `runAsync(Runnable)``supplyAsync(Supplier)` | 默认使用`ForkJoinPool.commonPool`线程池,也可通过`Executor`参数指定线程池 | `runAsync`无返回值,`supplyAsync`有返回值。调用`get()`,`join()`返回阻塞等待线程结束 |
| 两个线程一次执行 | `thenApply` | 获取前一个线程的结果,进行转换 | 有返回值 |
| `thenAccept` | 获取前一个线程的结果,消费 | 无返回值 | |
| `thenRun` | 忽略前一个线程的结果,执行额外的逻辑 | 无返回值 | |
| `whenComplete` | 获取前一个线程的结果或异常,消费 | 不影响上一线程的返回值 | |
| `exceptionally` | 前面线程异常时执行,一般跟`whenComplete`配合使用。捕获异常范围和前面所有异步线程,如:`thenApply().thenAccept().exceptionally()` | 有返回值 | |
| `handle` | 相当于`whenComplete`和`exceptionally`的组合。根据是否产生异常,内部`if else`分支处理业务逻辑 | 有返回值 | |
| 等待两个线程都执行完 | `thenCombine` | 2个线程都要有返回值,等待都结束,结果合并转换 | 有返回值 |
| `thenAcceptBoth` | 2个线程都要有返回值,等待都结束,结果合并消费 | 无返回值 | |
| `runAfterBoth` | 2个线程无需要有返回值,等待都结束,执行其他逻辑 | 无返回值 | |
| 等待两个线程任一执行完 | `applyToEither` | 2个线程都要有返回值,等待任一先结束,转换其结果 | 有返回值 |
| `acceptToEither` | 2个线程都要有返回值,等待任一先结束,消费其结果 | 无返回值 | |
| `runAfterEither` | 2个线程无需有返回值,等待任一先结束,执行其他逻辑 | 无返回值 | |
| 多个线程等待 | `CompletableFuture.anyOf(cf1,cf2,cf3).join()` | 多个任务任一执行完即返回 | 有返回值`Object` |
| `CompletableFuture.all(cf1,cf2,cf3).join()` | 多个任务全部执行完返回 | 无返回值 |
一、CompletableFuture 介绍
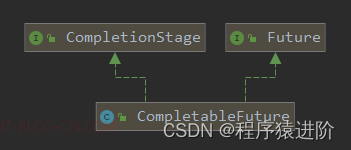
JDK1.8中的CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和加强。实现了CompletionStage和Future接口,前者是对后者的一个扩展,增加了异步回调、流式处理、多个Future组合处理的能力和通过回调的方式处理计算结果,使Java在处理多任务的协同工作时更加顺畅便利。
CompletionStage接口定义了任务编排的方法,可以向下执行后续阶段。异步执行的,默认线程池是ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),但为了业务之间互不影响,且便于定位问题,强烈推荐使用自定义线程池。
CompletableFuture中默认线程池如下:
// 根据commonPool的并行度来选择,而并行度的计算是在ForkJoinPool的静态代码段完成的
private static final boolean useCommonPool =
(ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism() > 1);
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
//forkJoinPool中初始化commonPool的参数
static {
// initialize field offsets for CAS etc
try {
U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class k = ForkJoinPool.class;
CTL = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("ctl"));
RUNSTATE = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("runState"));
STEALCOUNTER = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("stealCounter"));
Class tk = Thread.class;
……
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
commonMaxSpares = DEFAULT_COMMON_MAX_SPARES;
defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory =
new DefaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory();
modifyThreadPermission = new RuntimePermission("modifyThread");
// 调用makeCommonPool方法创建commonPool,其中并行度为逻辑核数-1
common = java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged
(new java.security.PrivilegedAction() {
public ForkJoinPool run() { return makeCommonPool(); }});
int par = common.config & SMASK; // report 1 even if threads disabled
commonParallelism = par > 0 ? par : 1;
}
二、异步操作
CompletableFuture提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作:
public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable) public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier) public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier, Executor executor)
4个方法详解:
【1】runAsync()以Runnable函数式接口类型为参数,没有返回结果,supplyAsync()以Supplier函数式接口类型为参数,返回结果类型为U;Supplier接口的get()是有返回值的(会阻塞)
【2】使用没有指定Executor的方法时,内部使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行
【3】默认情况下CompletableFuture会使用公共的ForkJoinPool线程池,这个线程池默认创建的线程数是CPU的核数(也可以通过JVM option:-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism来设置ForkJoinPool线程池的线程数)。如果所有CompletableFuture共享一个线程池,那么一旦有任务执行一些很慢的I/O操作,就会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在I/O操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,进而影响整个系统的性能。所以,强烈建议你要根据不同的业务类型创建不同的线程池,以避免互相干扰
异步操作
Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("无返回结果异步任务");
CompletableFuture.runAsync(runnable);
CompletableFuture future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("有返回值的异步任务");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Hello World";
});
String result = future.get();
join()和get()方法都是用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值。join()方法抛出的是uncheck异常(即未经检查的异常),不会强制开发者抛出。get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException需要用户手动处理, 抛出或者 try catch
结果处理: 当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,我们可以执行特定的Action。主要是下面的方法:
public CompletableFuture whenComplete(BiConsumer other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage other,Runnable action);
CompletableFuture future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(5);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(5);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
future1.runAfterEither(future2, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("已经有一个任务完成了");
}
}).join();
anyOf
anyOf()的参数是多个给定的CompletableFuture,当其中的任何一个完成时,方法返回这个CompletableFuture。
public static CompletableFuture anyOf(CompletableFuture... cfs)
Random random = new Random();
CompletableFuture future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(5));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello";
});
CompletableFuture future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "world";
});
CompletableFuture result = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
allOf
allOf方法用来实现多CompletableFuture的同时返回。
public static CompletableFuture allOf(CompletableFuture... cfs)
CompletableFuture future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1完成!");
return "future1完成!";
});
CompletableFuture future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("future2完成!");
return "future2完成!";
});
CompletableFuture combindFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);
try {
combindFuture.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
七、使用案例
实现最优的“烧水泡茶”程序。著名数学家华罗庚先生在《统筹方法》这篇文章里介绍了一个烧水泡茶的例子,文中提到最优的工序应该是下面这样:
T1 流程:洗水壶(1分钟) -> 烧开水(15分钟) ->
-> 泡茶(结果)
T2 流程:洗茶壶(1分钟) -> 洗茶杯(2分钟) -> 拿茶叶(1分钟)
对于烧水泡茶这个程序,一种最优的分工方案:用两个线程 T1 和 T2 来完成烧水泡茶程序,T1 负责洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶这三道工序,T2 负责洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶三道工序,其中 T1 在执行泡茶这道工序时需要等待 T2 完成拿茶叶的工序。
基于Future实现
public class FutureTaskTest{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建任务T2的FutureTask
FutureTask ft2 = new FutureTask(new T2Task());
// 创建任务T1的FutureTask
FutureTask ft1 = new FutureTask(new T1Task(ft2));
// 线程T1执行任务ft2
Thread T1 = new Thread(ft2);
T1.start();
// 线程T2执行任务ft1
Thread T2 = new Thread(ft1);
T2.start();
// 等待线程T1执行结果
System.out.println(ft1.get());
}
}
// T1Task需要执行的任务:
// 洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶
class T1Task implements Callable {
FutureTask ft2;
// T1任务需要T2任务的FutureTask
T1Task(FutureTask ft2){
this.ft2 = ft2;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15);
// 获取T2线程的茶叶
String tf = ft2.get();
System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:"+tf);
System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
return "上茶:" + tf;
}
}
// T2Task需要执行的任务:
// 洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶
class T2Task implements Callable {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
return "龙井";
}
}
基于CompletableFuture实现
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任务1:洗水壶->烧开水
CompletableFuture f1 = CompletableFuture
.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
sleep(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
//任务2:洗茶壶->洗茶杯->拿茶叶
CompletableFuture f2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
sleep(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return "龙井";
});
//任务3:任务1和任务2完成后执行:泡茶
CompletableFuture f3 = f1.thenCombine(f2, (__, tf) -> {
System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:" + tf);
System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
return "上茶:" + tf;
});
//等待任务3执行结果
System.out.println(f3.join());
}
static void sleep(int t, TimeUnit u){
try {
u.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}





还没有评论,来说两句吧...